Atoms Are Neutral Because The Number Of
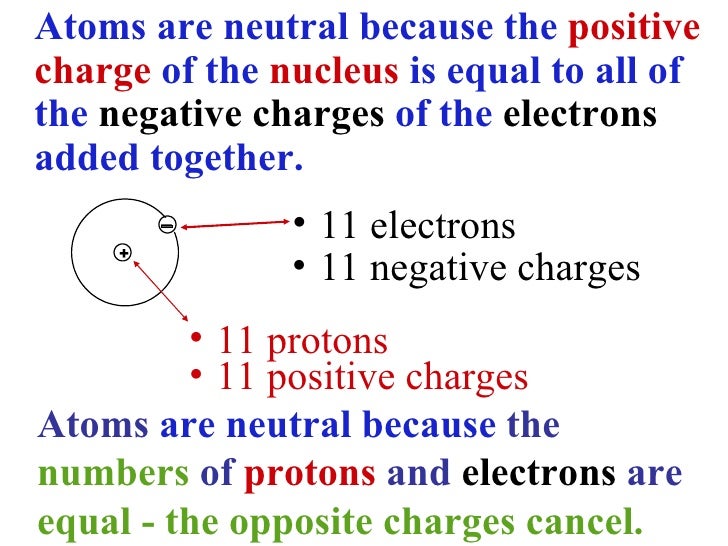
Atoms are neutral because they have same number of positively charged particles, protons, and negatively charged particles, electrons. The amount of charge in a single proton is equal to the amount of charge possessed by a single electron. Atoms also have another particle type in the nucleus called neutrons that have no charge.
- How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in a specific kind of atom? First, if an atom is electrically neutral overall, then the number of protons equals the number of electrons. Because these particles have the same but opposite charges, equal numbers cancel out, producing a neutral atom.
- Atoms are the fundamental building blocks of all matter and are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Because atoms are electrically neutral, the number of positively charged protons must be equal to the number of negatively charged electrons.
An atom is considered the most basic unit of matter, and it is considered neutral or neutrally-charged simply because it contains the same numbers of protons and electrons. Â Protons and electrons have opposite charges, but they basically cancel out each other making the charge neutral.
Because Atoms Are Electrically Neutral The Number Of Protons And
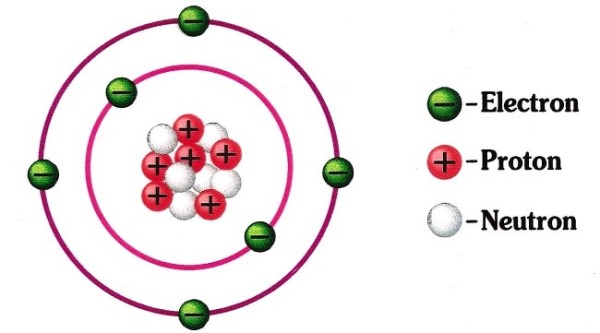
There are actually three particles that make up an atom and these are; neutrons, protons, and electrons. Â The outer part of an atom is formed by multiple electrons that have negative charges. Â The inner portion, called the nucleus, is meanwhile composed of the other two particles called protons and neutrons. Neutrons are those that have a neutral charge as the name suggests. Â Protons, meanwhile, contain a positive electrical charge. Â For a typical atom, the number of protons at the nucleus always equals the number of electrons that surround them. So even if the protons and electrons contain opposite electrical charges, they wouldn’t be able to cause a reaction because their charges will even out with each other. Â Because of this configuration in terms of the proton and electron charge, the atom will contain a neutral charge.
Under normal conditions, the placement of atomic particles stays where it is, and that is referring to the protons and neutrons lying at the center, or nucleus, while the electrons are formed on the outside parts. Â This basic atomic structure is said to be maintained by an electromagnetic force. Â If there is no such force, then the particles will not be bound together. Â In the same way, all atoms that are electromagnetically bound together form a bigger substance called a molecule. Â The charge for a molecule depends on whether the atoms combined are positively or negatively charged. Â Atoms that are positively charged or negatively charged become an ion. Â But in standard conditions, the charge of an atom remains neutral because of the equal number of positive protons and negative electrons.
Author: Hari M

Why Are Atoms Considered Neutral